Complete guide to Next 12 and Prepr personalization
Estimated duration: 20 minutes
This guide shows you how to connect Prepr to a Next project including styling and personalization. You can then customize this project to fit the requirements for your web app.
Introduction
This is a step-by-step guide that shows you how to set up a working front-end app with personalization. By using Next for the front end you will connect to Prepr content that’s set up with personalization.
You are going to build this front end in the following steps:
- Step 1 Create a new Next project - In this first step you'll install a working Next project.
- Step 2 Install Tailwind - You'll add built-in styling by installing Tailwind.
- Step 3 Create a static page - At the end of this step, you'll have a working website with static content.
- Step 4 Install the Apollo client - This step allows the front end to connect to Prepr and retrieve content dynamically.
- Step 5 Make the page dynamic - At the end of this step, you'll see a working app displaying the content from Prepr.
- Step 6 Set up personalization - In the final step you add personalization to Prepr content and make simple updates to the front end to personalize the web app page.
At the end of this guide, you’ll have a working website with personalization like the image below. On the left, you can see a site connected to Prepr with a home page. On the right is the same page that has been personalized for a specific target audience (Beginner bakers).
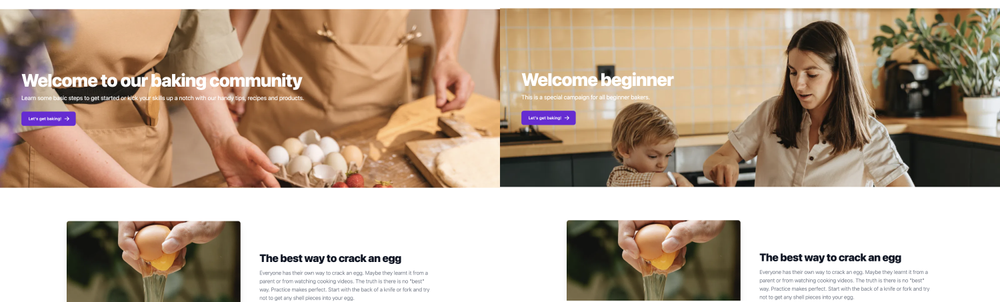
Visit our demo website to see a personalization example in action (opens in a new tab).
Prerequisites
You need to have the following setup before you connect your Next project to Prepr.
- A free Prepr account (opens in a new tab)
- An environment with demo data in Prepr
- The latest version of Node.js (opens in a new tab).
Check out the Next Complete starter repository on GitHub (opens in a new tab) for the full code used in this guide. The code referenced in this guide is a simplified subset of the Page pattern in the repo so there'll be some differences.
Step 1: Create a new Next project
This guide is based on Next.js version 12. The instructions below will guide you on how to create an empty Next project for your app.
If you have an existing Next.js project then you can skip this step.
- Open a terminal and execute the following command to create a new Next project called
prepr-personalization:
npx create-next-app@12 prepr-personalization && npm i next@12- When the project is successfully created, go to the
prepr-personalizationfolder, the root directory of the project, and execute the following command:
npm run dev-
You should now be able to view your app on your localhost, for example,
http://localhost:3000/. -
Open the Next project with your preferred code editor.
-
Update the
index.jsin thepagesfolder with the code below to display your page.
export default function Home() {
return (
<div>
<h1>My home page</h1>
</div>
);
}You should now see something like the image below on your localhost.

Once your Next project is created and working, add some styling.
Step 2: Install Tailwind
Tailwind is an extensive library of UI components that can be reused in a front end or design project. Use Tailwind CSS packages (opens in a new tab) for the styling in this project.
- Stop the server you started in the above step (
CTRL-C) and execute the following commands in the terminal to install Tailwind:
npm install -D tailwindcss postcss autoprefixer
npx tailwindcss init -p- Configure Tailwind in the
tailwind.config.jsfile with the following code:
/** @type {import('tailwindcss').Config} */
module.exports = {
// List the files that will use tailwind classes
content: [
'./pages/**/*.{js,ts,jsx,tsx,mdx}',
'./components/**/*.{js,ts,jsx,tsx,mdx}',
],
theme: {
extend: {},
},
plugins: [],
};- Go to the
styles/globals.cssfile to add the Tailwind CSS directives with the following code:
@tailwind base;
@tailwind components;
@tailwind utilities;- Test the Tailwind installation by adding styling to the heading in the
index.jsfile in thepagesfolder as follows:
export default function Home() {
return (
<div>
{/* Add styling to the heading */}
<h1 className="mb-4 bg-black text-3xl font-extrabold text-white md:text-6xl lg:text-6xl">
My home page
</h1>
</div>
);
}Now, when you visit the localhost, you should see a styled heading in your app like in the image below:

Step 3: Create a static page
In this step, you'll create a static version of the page including two front-end components. Later, you'll update them to fetch the corresponding data dynamically from Prepr.
As you can see in the image below, there is a Home page content item in the demo data in Prepr. The Home page has all the elements of the page in a Stack field. The stack makes it easy for an editor to set up their page content in a flexible structure for the front end. Check out the page pattern doc for more details on how to use the Stack field.
For this project, you are going to implement this page and two components: Page header and Image and text. In this step, you'll first implement these as static components. Later in the guide, you'll retrieve the content for these components from Prepr to make them dynamic.
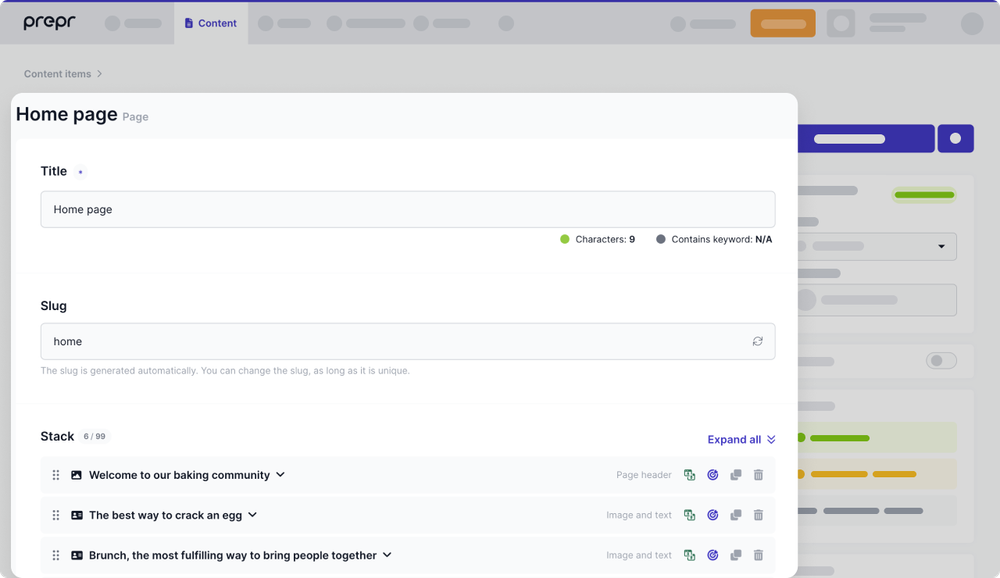
Add the components to the front end as follows:
- Update the
index.jsfile with the following code to display the components with static data:
// Make the components available in the code below
import PageHeader from '@/components/page-header';
import ImageAndText from '@/components/image-and-text';
export default function Home() {
return (
<div>
{/* Set data fields to static values for the Page and header and the image and text */}
<PageHeader
key="1"
text="This is static placeholder text."
heading="My static site"
image="https://placehold.co/1320x400?text=Page%20header%20image"
cta_label="Get more info"
/>
<ImageAndText
key="2"
image_position="right"
image_url="https://placehold.co/150x150?text=Image%20and%20Text%20image"
image_name="Placeholder image"
title="Static text title"
text="Static text body"
/>
</div>
);
}-
In the root directory of your Next project create a
componentsfolder with new files calledpage-header.jsandimage-and-text.js. -
Copy the code below into the
page-header.jsfile to construct the page header.
export default function PageHeader({ text, heading, image, cta_label })
{
return (
<>
{/* Set background image to the passed image variable */}
<section
style={{ backgroundImage: `url(${image})` }}
className='mb-12 flex items-center h-[600px] bg-no-repeat bg-cover'
>
<div className='container mx-auto md:px-0'>
<h1 className='mb-4 text-3xl font-extrabold leading-none tracking-tight text-white md:text-6xl md:text-5xl lg:text-6xl'>
{/* Set heading to the matching variable */}
{heading}
</h1>
<p className='mb-8 text-base font-normal text-white md:text-lg lg:text-xl'>
{/* Set text to the matching variable */}
{text}
</p>
<a
href='#notify'
className='
inline-flex
items-center
px-6
py-3.5
text-sm
font-medium
text-center text-white
rounded-lg
bg-violet-700
hover:bg-violet-800
focus:ring-4 focus:outline-none focus:ring-violet-300
'
>
{/* Set CTA label to the matching variable */}
{cta_label}
<svg
className="w-5 h-5 ml-2 -mr-1"
fill="currentColor"
viewBox="0 0 20 20"
xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"
>
<path
fillRule="evenodd"
d="M10.293 3.293a1 1 0 011.414 0l6 6a1 1 0 010 1.414l-6 6a1 1 0 01-1.414-1.414L14.586 11H3a1 1 0 110-2h11.586l-4.293-4.293a1 1 0 010-1.414z"
clipRule="evenodd"
></path></svg>
</a>
</div>
</section>
</>
);
}- Copy the code below into the
image-and-text.jsfile to construct the image and text.
export default function ImageAndText({ image_position, image_name, image_url, text, title }) {
return (
<div className='container mx-auto md:px-0'>
<section className='bg-white'>
<div
className='items-center max-w-screen-xl gap-8 px-4 py-8 mx-auto xl:gap-16 md:grid md:grid-cols-2 sm:py-16 lg:px-6'
>
{/* Set image URL to the matching variable */}
<img
className= {((image_position == 'Right') ? 'order-last' : 'order-first') + ' object-cover w-full rounded-lg shadow-xl h-60 md:h-96'}
src={image_url}
/>
<div className='mt-8 md:mt-4 md:mt-0'>
<h2
className='mb-4 text-xl font-extrabold tracking-tight text-center text-gray-900 md:text-left md:text-4xl'>
{/* Set title to the matching variable */}
{title}
</h2>
<p className='font-light text-center text-gray-500 md:mb-6 md:text-left md:text-lg'>
{/* Set text body to the matching variable */}
{text}
</p>
</div>
</div>
</section>
</div>
);
}You should now see something like the image below on your localhost:
Great work on getting your static web app working! Continue the following steps to make it dynamic by including data from Prepr.
Step 4: Install the Apollo client
The Apollo client is an integration tool that helps to retrieve CMS data with GraphQL. The instructions below show you how to install the Apollo client so that you can add GraphQL queries to request data from the Prepr API.
- Stop the server you started in the above step (
CTRL-C) and execute the following command in the terminal:
npm install @apollo/client graphql- Create a
servicesfolder in the root directory of the project. Then, create a file calledapollo-client.jsin this folder. Copy the following code to this file to import and initialize the Apollo client:
import { ApolloClient, InMemoryCache } from "@apollo/client";
const client = new ApolloClient({
uri: `https://graphql.prepr.io/${process.env.PREPR_ACCESS_TOKEN}`,
cache: new InMemoryCache(),
});
export default client;This client will be used to make API requests to endpoints provided by the Prepr CMS across your Next application.
- Get an access token by logging into your Prepr account:
a. Go to Settings → Access tokens to view all the access tokens.
b. Copy the GraphQL Production access token to only retrieve published content items.
Use the GraphQL Production access token to request published content items for your live app and use the GraphQL Preview token to make a preview of unpublished content items for your content editors.
We recommend using environment variables to store sensitive information like access tokens.
- To add environment variables, create a
.envfile in the root directory of your project and add the access token like this:
PREPR_ACCESS_TOKEN=<YOUR-ACCESS-TOKEN>- Execute the following commands to make sure that the Apollo client is installed correctly:
npm install
npm run devIf the app runs without errors, then the setup above was done correctly. The next step is to fetch content from Prepr using the installed Apollo client.
Once the apollo client is installed successfully, you can fetch the Home page content from Prepr using GraphQL queries.
Step 5: Make the page dynamic
Now that your Apollo client is installed and connected to Prepr, fetch the page content from Prepr.
Add a GraphQL query
First, create a query to get the content from Prepr as follows:
-
Create a
queriesfolder in the root directory of your project and create a file namedget-page-by-slug.js. -
Add the following query to this file to retrieve a page by its slug:
import { gql } from '@apollo/client';
export const GetPageBySlug = gql`
query ($slug: String) {
Page(slug: $slug) {
_id
title
_slug
# Retrieve the stack and two components:
# Page Header and Image and Text
stack {
__typename
... on PageHeader {
heading
cta_url
cta_label
image {
url(width: 1600)
}
_id
text
}
... on ImageAndText {
image {
url(width: 800)
}
text
title
image_position
_id
}
}
}
}
`;You can create and test GraphQL queries using the Apollo explorer (opens in a new tab) from Prepr. Open the API Explorer from the Article content item or the access token that you copied previously.
- Test the query by updating the
index.jsfile in thepagesfolder. In this code, execute the query and print the query results to the console as follows:
import PageHeader from '@/components/page-header';
import ImageAndText from '@/components/image-and-text';
// Make the apollo client and query available in the code
import client from '../services/apollo-client';
import { GetPageBySlug } from '../queries/get-page-by-slug';
// Include an argument for the page that is fetched from Prepr
export default function Home({page}) {
return (
<div>
<PageHeader
key="1"
text="This is static placeholder text."
heading="My static site"
image="https://placehold.co/1320x400?text=Page%20header%20image"
cta_label="Get more info"
/>
<ImageAndText
key="2"
image_position="right"
image_url="https://placehold.co/150x150?text=Image%20and%20Text%20image"
image_name="Placeholder image"
title="Static text title"
text="Static text body"
/>
</div>
);
}
// The function executes the query, assigns a variable to the returned results and prints the results to the console
export async function getServerSideProps(context) {
// Execute the query and assign the results to a data variable
const { data} = await client.query({
query: GetPageBySlug,
variables: {
slug: "home",
},
fetchPolicy: 'no-cache',
});
// Print the query result to the console
console.log(JSON.stringify(data.Page, undefined, 2));
return {
props: { page: data.Page },
};
}If you’re using preloaded demo data in your Prepr environment as mentioned above in the Prerequisites section, you should have one home page with the slug home. The query will retrieve the id, title, slug, and a stack containing a page header and two image and text blocks with their own fields.
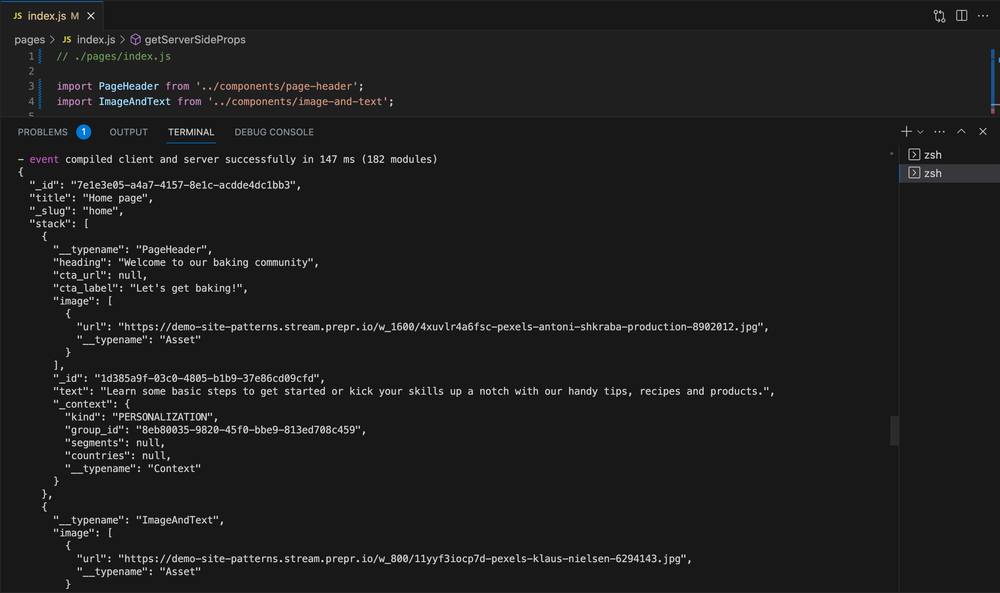
When you check the console in your terminal, the response to the query looks something like this:
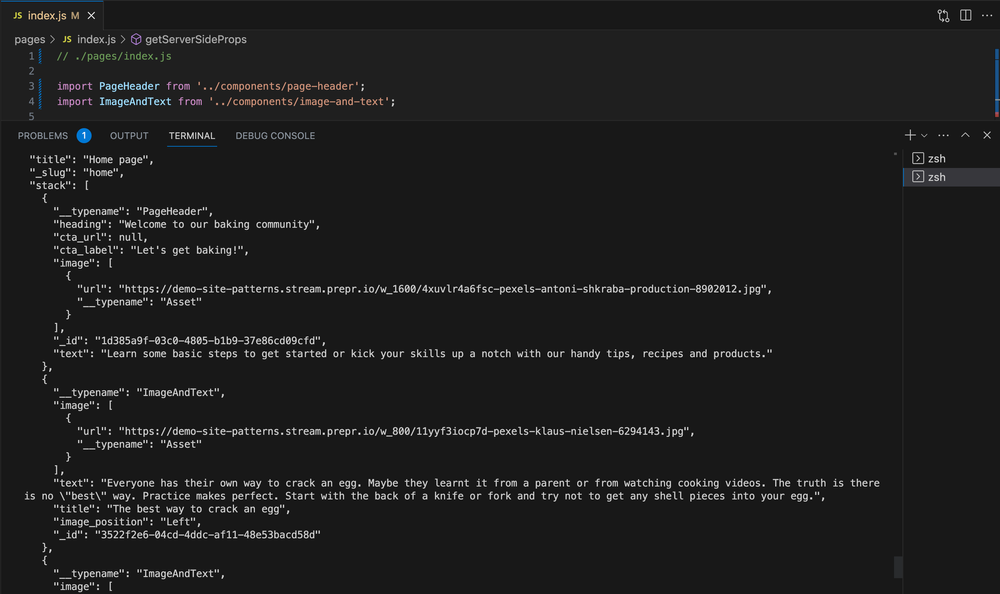
Now that the query has been created and retrieves the data successfully, fetch the specific page content from the query results.
Fetch page content
To view the Prepr content in the web app, you need to fetch the page elements. As mentioned previously, the page has elements in a Stack field. You'll fetch two components, Page header and Image and Text in the stack.
- Fetch and set the data for each of the components to build the page by updating the
Homefunction in theindex.jsas follows:
import PageHeader from '@/components/page-header';
import ImageAndText from '@/components/image-and-text';
import client from '../services/apollo-client';
import { GetPageBySlug } from '../queries/get-page-by-slug';
export default function Home({page}) {
// Map the individual fields from the retrieved Stack to each component
const stackFields = page.stack.map((element, index) => {
if (element.__typename === 'PageHeader') {
// Set and return the Page header values to the fetched data
return (
<PageHeader
key={index}
text={element.text}
heading={element.heading}
image={element.image[0]?.url}
cta_label={element.cta_label}
/>
);
} else if (element.__typename === 'ImageAndText') {
// Set and return the Image and text values to the fetched data
return (
<ImageAndText
key={index}
image_position={element.image_position}
image_url={element.image[0]?.url}
image_name={element.image[0].name}
title={element.title}
text={element.text}
/>
);
}
});
//Return all the mapped stack fields
return stackFields;
}
export async function getServerSideProps(context) {
const { data} = await client.query({
query: GetPageBySlug,
variables: {
slug: "home",
},
fetchPolicy: 'no-cache',
});
console.log(JSON.stringify(data.Page, undefined, 2));
return {
props: { page: data.Page },
};
}Now when you view the website on your localhost, you'll see something like the image below:
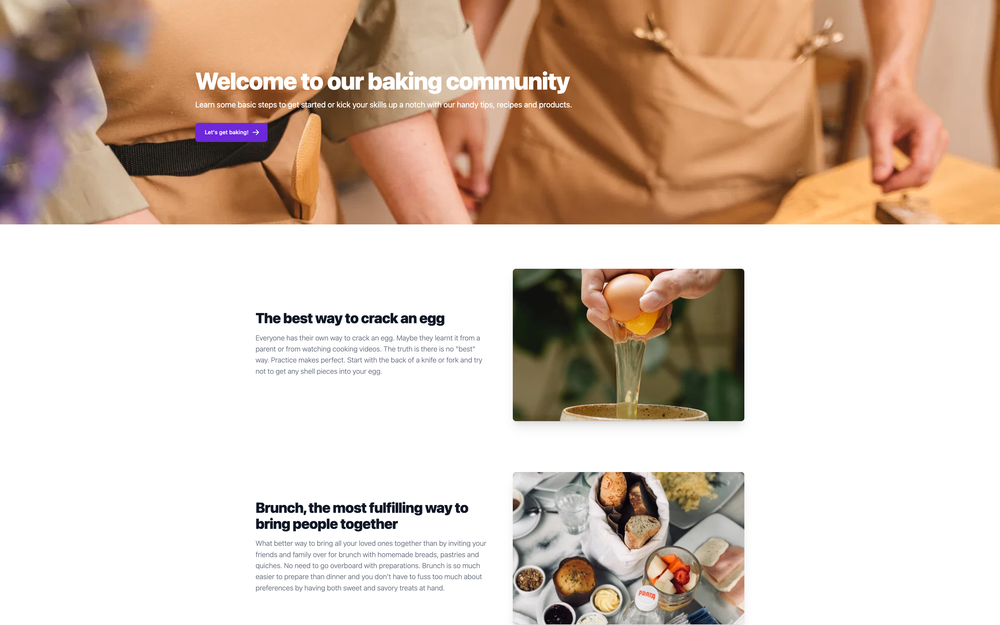
Congratulations! You have successfully connected your web app to Prepr. Go to your Home page content item in Prepr and make some content updates to see the effects on your web app immediately. For example, reorder the page header and the image and text blocks.
Step 6: Set up personalization
Now that you have a working web app with styling and content from Prepr, add personalization. Prepr lets you create personalized experiences with Adaptive content. With Adaptive content, content editors can make different versions of content for various customer segments. You can then show the right content to each visitor based on their segment giving them a personalized experience.
For this project, assume the scenario below for the baking community web app.
A user comes across a campaign for beginner bakers in a social post. They click the link in the post and get directed to your page. The URL link from this post includes a special UTM tag that identifies the specific campaign. Your web app uses the UTM tag to retrieve the adaptive content and display the personalized page for the beginner baker.
Start by personalizing the page header in Prepr.
Personalize the page header in Prepr
You want to show a different version of the page header when a beginner baker visits the page. The setup for personalization in Prepr is made up of two parts. First you need to create customer segments and then add the personalized content for that segment. If you are using the preloaded demo data then you already have some customer segments defined like in the image below.
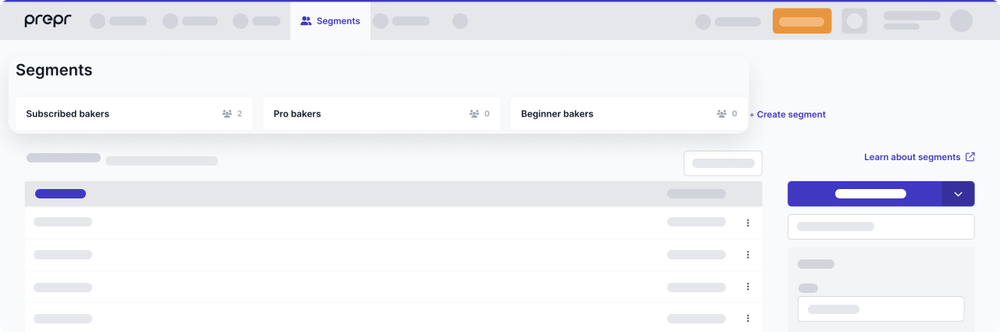
For this example, use the Beginner bakers segment. For more details, check out the Customer segments doc.
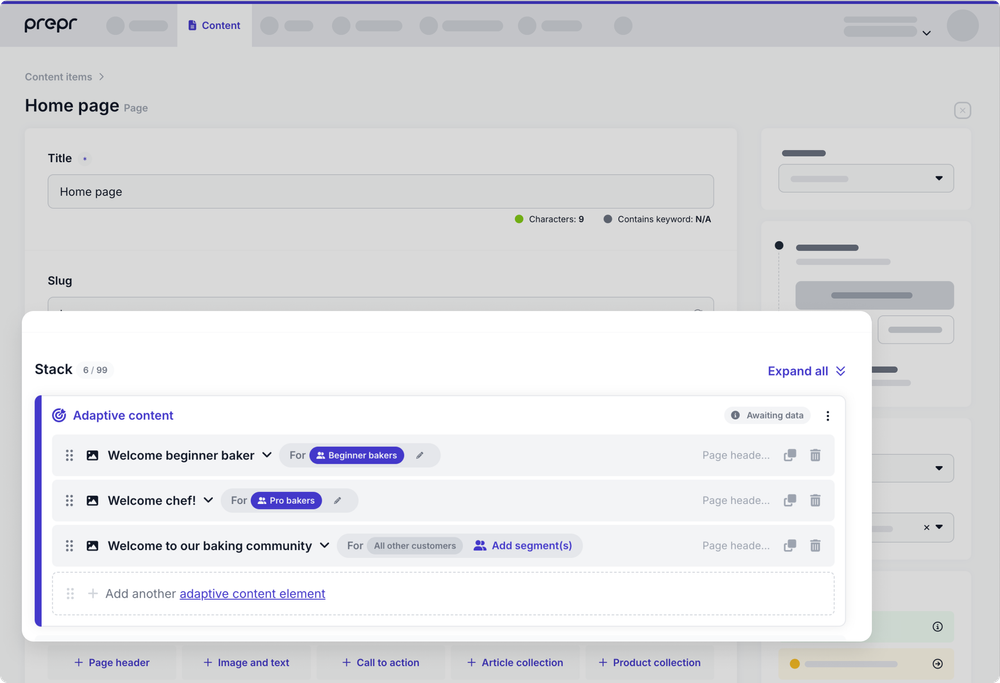
Go to your Home page content item in Prepr and add personalization as follows:
- Go to the page header in the stack and click the icon on the page header to personalize the element.
- Duplicate the page header. The original page header will automatically be used as the fallback content and linked to All other customers.
- Update the image and text for the Beginner bakers page header.
- Click the Add segment link and choose the Beginner bakers segment for this header and save the page.
Now that the adaptive content is ready, add some code to your front end.
Get the segment Id from the UTM tag
To fetch the personalized page, get the UTM tag from the URL. In this example, the UTM tag matches the segment Id for Beginner bakers.
Update the getServerSideProps function in the index.js file with the following code to get the UTM campaign value and to fetch the personalized content.
import PageHeader from '@/components/page-header';
import ImageAndText from '@/components/image-and-text';
import client from '../services/apollo-client';
import { GetPageBySlug } from '../queries/get-page-by-slug';
export default function Home({page}) {
const stackFields = page.stack.map((element, index) => {
if (element.__typename === 'PageHeader') {
return (
<PageHeader
key={index}
text={element.text}
heading={element.heading}
image={element.image[0]?.url}
cta_label={element.cta_label}
/>
);
} else if (element.__typename === 'ImageAndText') {
return (
<ImageAndText
key={index}
image_position={element.image_position}
image_url={element.image[0]?.url}
image_name={element.image[0].name}
title={element.title}
text={element.text}
/>
);
}
});
return stackFields;
}
export async function getServerSideProps(context) {
// Get the utm campaign from the URL parameters and map it to a segment variable
const { utm_campaign: segment } = context.query;
const { data} = await client.query({
query: GetPageBySlug,
variables: {
slug: "home",
// Also pass the segment value to the query making sure it's not undefined
segment: segment ||'',
},
fetchPolicy: 'no-cache',
});
console.log(JSON.stringify(data.Page, undefined, 2));
return {
props: { page: data.Page },
};
}Once that's done, update the query with the segment ID that you just defined.
Update the query
The current page query returns a page that is not personalized. So, you need to set a segment parameter in the query to get the personalized page. In this example, this value has to match the segment Id for Beginner bakers.
Update the query in the get-page-by-slug.js with this parameter and additional personalization fields as follows:
import { gql } from '@apollo/client';
export const GetPageBySlug = gql`
# Add variable for the segment
query ($slug: String, $segment: String!) {
Page(slug: $slug) {
_id
title
_slug
# Retrieve a variant based on the provided segment
stack (personalize_for_segments: [$segment]) {
__typename
... on PageHeader {
heading
cta_url
cta_label
image {
url(width: 1600)
}
_id
text
# Retrieve system fields with personalization info
# The _context fields hold info about the personalization:
# - "kind" shows that this component includes personalization
# - "group_id" is a unique Id to identify a specific personalized grouping for multiple personalized components
# - "segments" is the segment that the variant is applicable to.
# - "countries" is filled if the variant is applicable to specific countries.
_context {
kind
group_id
segments
countries
}
}
... on ImageAndText {
image {
url(width: 800)
}
text
title
image_position
_id
}
}
}
}
`;Now that the query has been updated to include personalized content, you can view the query results.
View in the browser
When you view the site as is, you should still see the page without personalized content. Check the console in your terminal for the updated results.
Add the UTM tag to the URL, for example:
http://localhost:3000/?utm_campaign=beginner-bakers
Now you can see the personalized content such as in the image below.
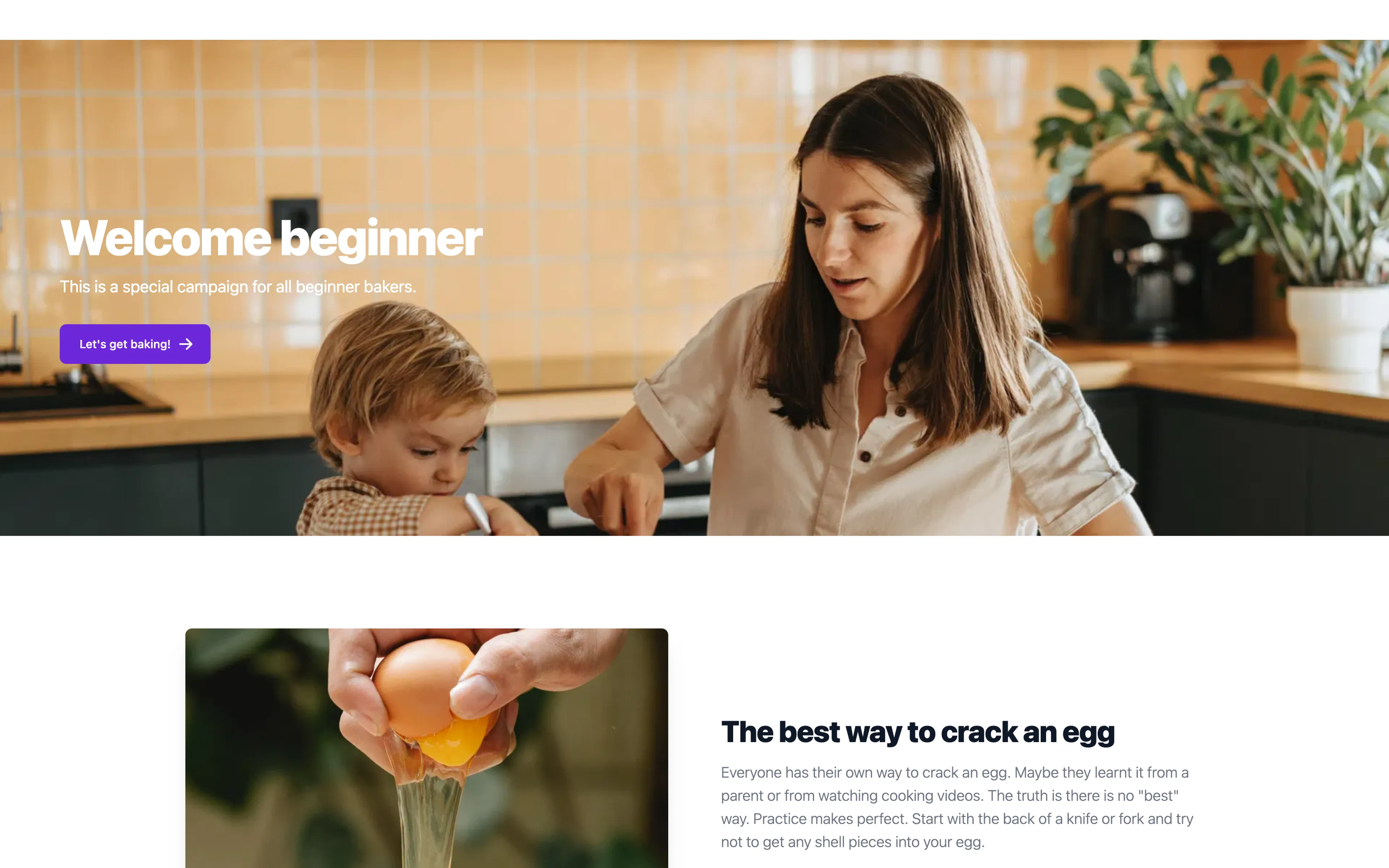
All done
Congratulations! You have a working Next web app connected to Prepr including personalization. This is a very simple example. You can personalize more elements like call-to-actions, featured articles and more. Also you can create dynamic segments based on what visitors do in your app. The options are limitless.
Next steps
To learn more on how to expand your project, check out the following resources:
Was this article helpful?
We’d love to learn from your feedback