Vue Quick start guide
Estimated duration: 10 minutes
This guide shows you how to connect Prepr to a Vue project to get data from Prepr CMS. You’ll learn how to make a simple blog with Vue and Prepr CMS. By the end of this guide, you’ll have a working app that looks like the image below.
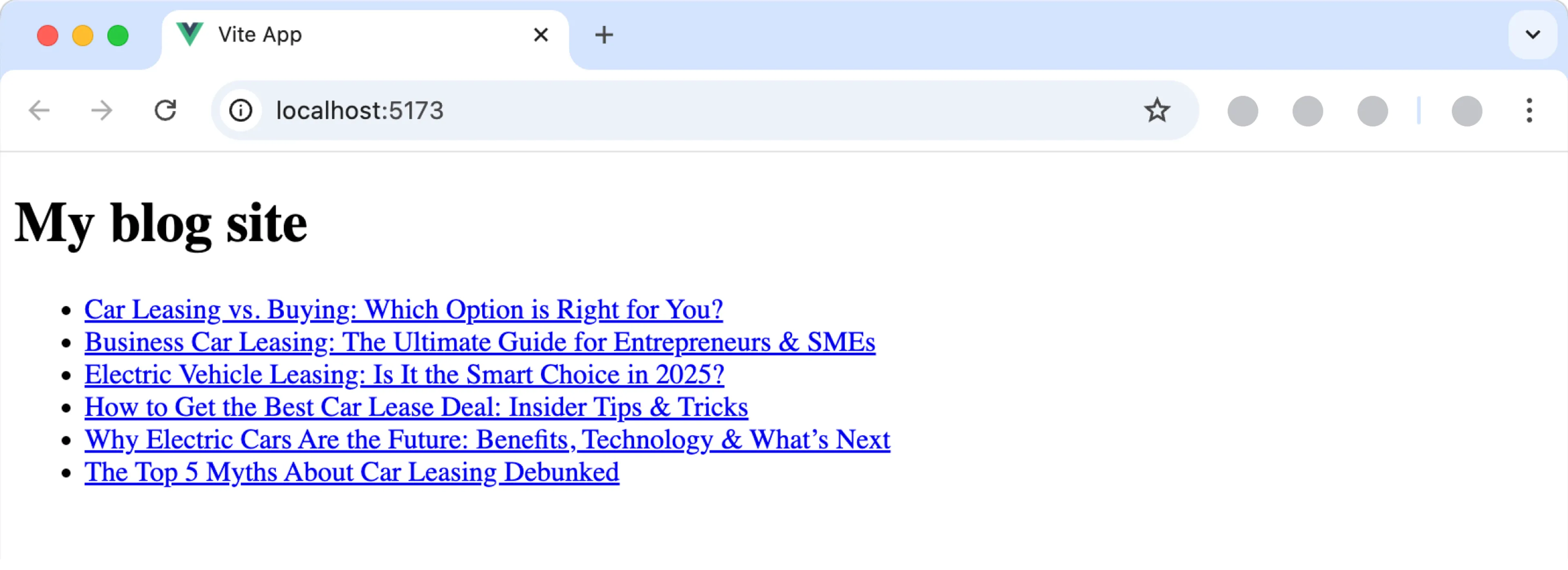
If you want to skip ahead, try out the zero installation demo on Stackblitz or clone the repository on GitHub to run the demo locally.
Prerequisites
You need to have the following setup before you connect your Vue project to Prepr.
Create a simple Blog website with Vue.js and Prepr CMS
Create a new Vue project
The instructions below will guide you on how to create an empty Vue project for your blog app.
If you have an existing Vue project then you can skip this step.
-
Open a terminal and execute the command below to create a new Vue project called
prepr-vue.npm init vue@latest prepr-vueGo to the
Router (SPA development)option and press the space bar to select it. This creates the same project structure used in this guide. -
When the project is successfully created, go to the
prepr-vuefolder, the root directory of the project, and start the project with the following commands in the terminal:cd prepr-vuenpm installnpm run dev -
You should now be able to view your app on your localhost, for example,
http://localhost:3000/. -
Open your Vue project with your preferred code editor.
-
Go to the
src/viewsfolder and replace the contents of theHomeView.vuefile with the following code to display a single heading:./src/views/HomeView.vue<template> <div> <h1>My blog site</h1> </div> </template> -
Replace the code in the
App.vuefile in thesrcfolder with the code below to remove the Vue welcome and formatting from the page../src/App.vue<script setup> import { RouterView } from 'vue-router' </script> <template> <RouterView /> </template> -
This project doesn’t include any styling, so go to the
src/assetsfolder and empty themain.cssfile to remove the existing styling.
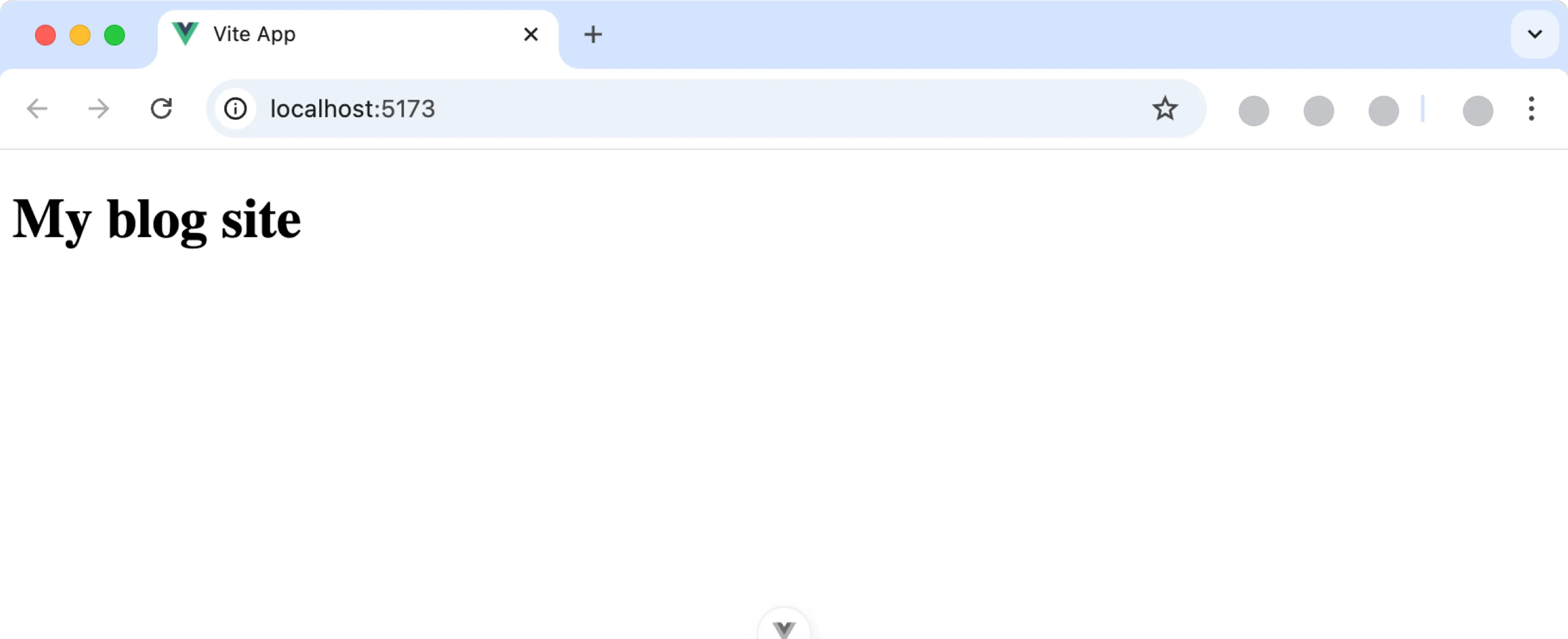
You should now see something like the image below on your localhost.
Install Apollo Client
Apollo Client is an integration tool that helps to retrieve CMS data with GraphQL. The instructions below show you how to install Apollo Client so that you can execute GraphQL queries to request data from the Prepr API.
-
Stop the server you started in the above step (
CTRL-C) and run the commands below in the terminal to install Apollo Client to execute GraphQL queries in a Vue project.npm install --save graphql graphql-tag @apollo/clientnpm install --save @vue/apollo-option @apollo/client -
Create a folder called
servicesin thesrcfolder. Then, create a file calledapollo-client.jsin this folder. Copy the following code to this file to import Apollo Client:./src/services/apollo-client.jsimport { ApolloClient, createHttpLink, InMemoryCache } from '@apollo/client/core' // HTTP connection to the API const httpLink = createHttpLink({ // You should use an absolute URL here uri: `https://graphql.prepr.io/${import.meta.env.VITE_PREPR_ACCESS_TOKEN}`, }) // Cache implementation const cache = new InMemoryCache() // Create the apollo client const apolloClient = new ApolloClient({ link: httpLink, cache, }) export default apolloClient; -
Add the code below to the
main.jsin thesrcfolder to import and create the Apollo Provider../src/main.jsimport { createApp } from 'vue' import App from './App.vue' import router from './router' // Import the Apollo provider and the apollo client import {createApolloProvider} from "@vue/apollo-option"; import apolloClient from "@/services/apollo-client"; // Initiate the Apollo provide const apolloProvider = createApolloProvider({ defaultClient: apolloClient, }) const app = createApp(App) app.use(router) //Include the Apollo Provider in the app app.use(apolloProvider) app.mount('#app') -
We recommend using environment variables to store sensitive information like access tokens. To add environment variables, create a
.envfile in the root directory of your project and add the access token like this:./.envVITE_PREPR_ACCESS_TOKEN=<YOUR-ACCESS-TOKEN> -
Replace the placeholder value
<YOUR-ACCESS-TOKEN>with an access token from Prepr. Get an access token by logging into your Prepr account:
a. Click the icon and choose the Access tokens option to view all the access tokens.
b. Copy the GraphQL Production access token to only retrieve published content items on your site.
Use the GraphQL Production access token to request published content items for your live app and use the GraphQL Preview token to make a preview of unpublished content items for your content editors.
-
Execute the following command to make sure that Apollo Client is installed correctly:
npm run dev
If your app runs without errors, then the setup above was done correctly. The next step is to fetch content from Prepr using the installed Apollo Client.
Fetch multiple blog posts
Now that Apollo lient is installed and connected to Prepr, fetch the blog posts from Prepr.
Add a GraphQL query
-
Go to the
srcfolder and create aqueriesdirectory. In here, create a file namedget-posts.js. -
Add the following query to this file to retrieve all blog posts:
./src/queries/get-posts.jsimport gql from 'graphql-tag' export const GetPosts = gql` query { Posts { items { _id _slug title } } } `You can create and test GraphQL queries using the Apollo explorer from Prepr. Open the API Explorer from the Post content item page in Prepr or the access token page.
If you’re using preloaded demo data in your Prepr CMS environment as mentioned above in the Prerequisites section, you should have a few published blog posts as shown in the below image. The query will retrieve the ID, Slug, and Title of each blog post.
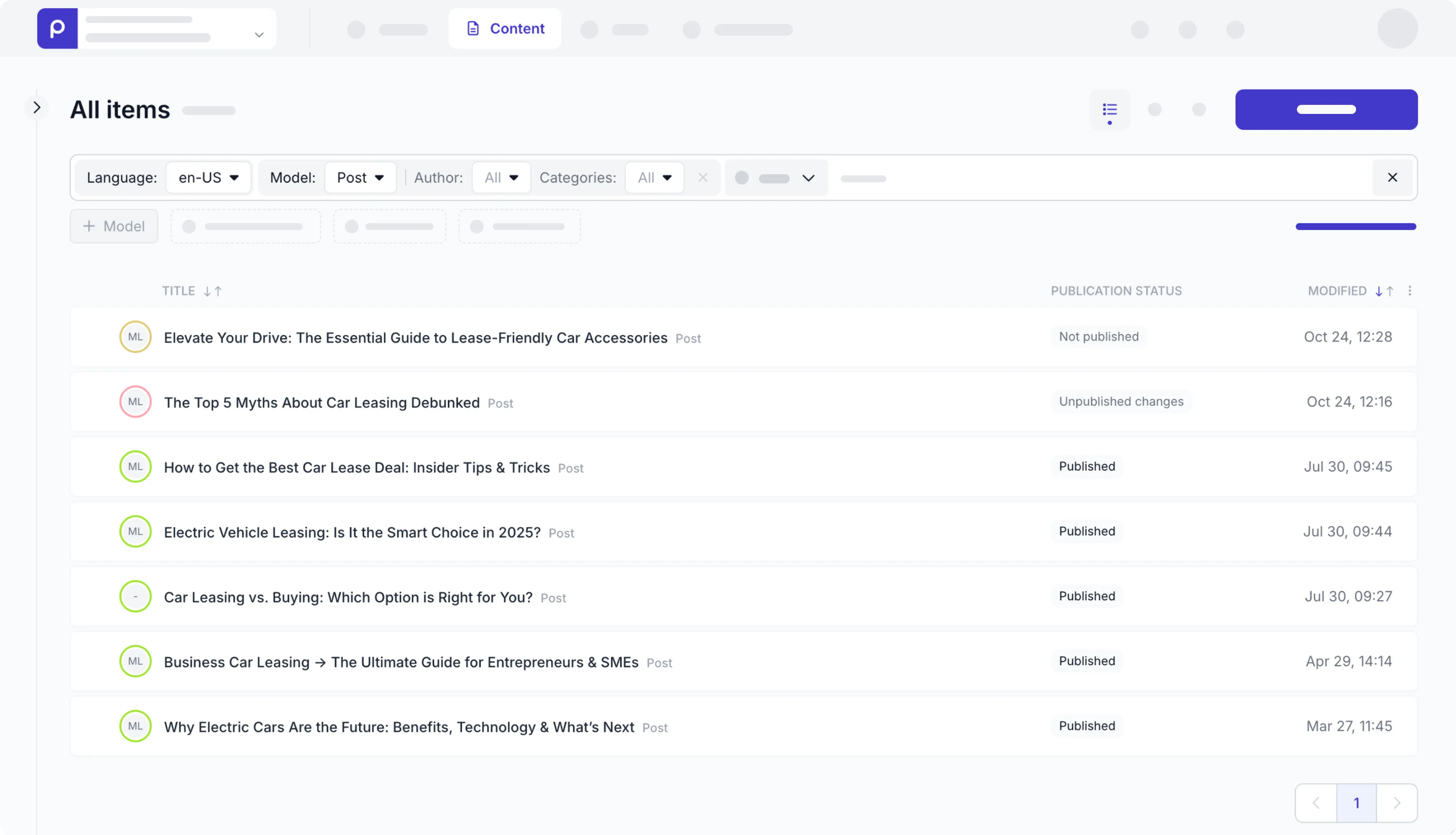
In the next step, we’ll fetch and process the query response.
Fetch data
Now that the query has been added, fetch the blog posts from Prepr and display them in the app.
- Open the
HomeView.vuefile and add a script and HTML to execute the query and display the query results with the code below.
<script>
import {GetPosts} from "@/queries/get-posts";
export default {
apollo: {
Posts: GetPosts
},
data() {
return {
Posts: ''
}
},
}
</script>
<template>
<div>
<h1>My blog site</h1>
<ul v-if="Posts">
<li v-for="post in Posts.items" :key="post._id">
<router-link :to="post._slug">{{post.title}}</router-link>
</li>
</ul>
</div>
</template>Now when you view the website on your localhost, you’ll see something like the image below.

Fetch individual blog posts
Now you have the list of blog posts with links to them. When a visitor clicks a blog post link, your app should open a detailed post page automatically.
However, we haven’t created the detailed page yet. Now, when you click the link, an empty page opens with the slug in the URL.
The instructions below show you how to create a route from the main page to the detailed page and how to fetch the blog post details based on the slug of the blog post that was clicked.
Create dynamic routing
-
We added the Vue router as part of the installation, so adding routing is simple. Just update the
index.jsfile in therouterfolder to add a route to the detailed blog post page as follows:./src/router/index.jsimport { createRouter, createWebHistory } from 'vue-router' import HomeView from '../views/HomeView.vue' // import the detailed blog post page import PostView from "@/views/PostView.vue"; const router = createRouter({ history: createWebHistory(), routes: [ { path: '/', name: 'home', component: HomeView }, // Include routing to the detailed blog post page with the slug from the URL { path: '/:slug', name: 'post', component: PostView } ] }) export default router
Continue with the next step to fetch the post details and display the page.
Fetch post details
Add another query to fetch a specific blog post by its slug and make this page visible when clicking the link for a post.
-
Create a file called
get-post-by-slug.jsin thequeriesfolder and add the following query to this file to query a specific blog post by its slug:./src/queries/get-post-by-slug.jsimport gql from 'graphql-tag' export const GetPostBySlug = gql` query ($slug: String) { Post (slug: $slug) { _id title cover { url(width: 300, height: 250) } content { __typename ... on Text { _id body text } ... on Assets { items { _id url(width: 300, height: 250) } } } } } `
Now that the query is added, fetch the individual blog post by its slug. Fetch the title, cover image and the post content.
The Blog post content is stored in a Dynamic content field. Check out the GraphQL docs for more details on how to fetch the data within this field.
-
Open the
viewsfolder and create a new filePostView.vuewith the following code:./src/views/PostView.vue<script> import {GetPostBySlug} from "@/queries/get-post-by-slug"; export default { data() { return { Post: null, } }, apollo: { Post: { query: GetPostBySlug, variables () { return { slug: this.$route.params.slug } } } }, } </script> <template> <h1>{{Post.title}}</h1> <div class="my-10"> <img :src="Post.cover.url" :alt="`Image for ${Post.title}`" /> </div> <div :key="contentType._id" v-for="contentType in Post.content"> <!-- Display images if they exist --> <div v-if="contentType.__typename === 'Assets'" class="my-10"> <img v-if="contentType.items.length" :src="contentType.items[0]?.url" :alt="`Image for ${Post.title}`" /> </div> <!--Display the text in HTML format --> <div v-if="contentType.__typename === 'Text'" v-html="contentType.body" ></div> </div> </template>
Now, when you view your site, you can click any link to direct you to that specific blog post like in the image below.
All done
Congratulations! You have successfully connected a Vue project to Prepr for a simple Blog app.
Next steps
To learn more on how to expand your project, check out the following resources: